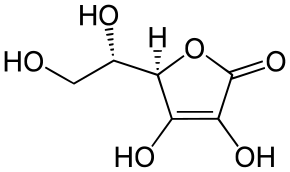
Аскарбінавая кіслата
Аскарбінавая кіслата, вітамін C (Acidum ascorbinicum) C6H8O6 — арганічнае злучэнне, роднаснае глюкозе. Выконвае важную ролю ў жыццядзейнасці арганізма чалавека і жывёл. Адыгрывае важную ролю ў акісляльна-аднаўленчых працэсах, садзейнічае працэсу ўтварэння дэзоксірыбануклеінавай кіслаты.

Бясколернае крышталічнае рэчыва, кіслае на смак. Малекулярная маса 176,13. Добра раствараецца ў вадзе, раствараецца ў этаноле. Амаль не раствараецца ў эфіры, бензоле, хлараформе, тлушчах. Растворы аскарбінавай кіслаты хутка акісляюцца на паветры.
Арганізм чалавека, прыматаў, марскіх свінак, некаторых птушак і рыб не здольны сінтэзаваць аскарбінавую кіслату. Неабходная колькасць яе здабываецца з ежы. Недахоп аскарбінавай кіслаты ў арганізме вядзе да захворвання цынгой.
Крыніцы аскарбінавай кіслаты
[правіць | правіць зыходнік]Аскарбінавая кіслата ўтрымліваецца ў ягадах, агародніне, садавіне, ігліцы хвоі і елкі. У медыцынскіх мэтах аскарбінавую кіслату атрымліваюць сінтэтычна з глюкозы.
Крыніцы
[правіць | правіць зыходнік]- ↑ Vitamin C — 2015.
- ↑ Vitamin C Праверана 9 кастрычніка 2015.
- ↑ а б Global Substance Registration System Праверана 14 лютага 2018.
- ↑ Bradley J., Williams A. J., Andrew S.I.D. Lang Jean-Claude Bradley Open Melting Point Dataset // Figshare — 2014. — doi:10.6084/M9.FIGSHARE.1031637.V2
- ↑ RxNorm Праверана 14 лютага 2018.
- ↑ Recommended INN: List 3 // Recommended INN: List 3 — 1959.
- ↑ The Politics of Khat Control — 2014. — doi:10.5040/9781474215718.CH-010
- ↑ Morton J. F. Rooibos tea,aspalathus linearis, a caffeineless, low-tannin beverage // Econ. Bot. — Springer Science+Business Media, 1983. — Vol. 37, Iss. 2. — P. 164–173. — ISSN 0013-0001; 1874-9364 — doi:10.1007/BF02858780
- ↑ Bährle-Rapp M. Filipendula ulmaria — 2010. — С. 206–206. — doi:10.1007/978-3-540-71095-0_3994
- ↑ Hasegawa N. Vitamin C is one of the lipolytic substances in green tea // Phytother. Res. / A. Izzo — Wiley, 2002. — Vol. 16 Suppl 1, Iss. S1. — P. S91–2. — ISSN 0951-418X; 1099-1573 — doi:10.1002/PTR.843
- ↑ M.-Y Ding, P.-R Chen, G.-A Luo Simultaneous determination of organic acids and inorganic anions in tea by ion chromatography // J. Chromatogr. A — Elsevier BV, 2002. — Vol. 764, Iss. 2. — P. 341–345. — ISSN 1873-3778; 0021-9673 — doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(96)00910-7
- ↑ D Palevitch, Craker L. E. Nutritional and Medical Importance of Red Pepper (Capsicum spp.) // Journal of Herbs, Spices and Medicinal Plants — Taylor & Francis, 2005. — Vol. 3, Iss. 2. — P. 55–83. — ISSN 1049-6475; 1540-3580 — doi:10.1300/J044V03N02_08
- ↑ Banga I, Szent-Györgyi A The large scale preparation of ascorbic acid from Hungarian pepper (Capsicum annuum). // Biochem. J. — London [etc.]: Portland Press, 1934. — Vol. 28, Iss. 5. — P. 1625–1628. — ISSN 0264-6021; 1470-8728 — doi:10.1042/BJ0281625
- ↑ Compadre C. M., A. Kinghorn The intensely sweet herb, Lippia dulcis Trev.: historical uses, field inquiries, and constituents // J. Ethnopharmacol. — Elsevier BV, 1986. — Vol. 15, Iss. 1. — P. 89–106. — 18 p. — ISSN 0378-8741; 1872-7573 — doi:10.1016/0378-8741(86)90105-4
- ↑ а б в г A. Rotundo, G. Bounous, S. Benvenuti et al. Quality and yield of ribes and rubus cultivars grown in Southern Italy hilly locations // Phytother. Res. / A. Izzo — Wiley, 1998. — Vol. 12, Iss. S1. — P. S135–S137. — ISSN 0951-418X; 1099-1573 — <S135::AID-PTR275>3.0.CO;2-H doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1573(1998)12:1+<S135::AID-PTR275>3.0.CO;2-H
- ↑ а б в г д е ё G. Vampa, S. Benvenuti, M. Melegari HPTLC Determination of Ascorbic Acid in Fruits of the GeneraRibes,Rubus, andVaccinium // Planta Med. — Thieme Medical Publishers (Germany), 2008. — Vol. 58, Iss. S 1. — P. 675–675. — ISSN 0032-0943; 1439-0221 — doi:10.1055/S-2006-961690
- ↑ Tausz M. Simultaneous Determination of Ascorbic Acid and Dehydroascorbic Acid in Plant Materials by High Performance Liquid Chromatography — <69::AID-PCA290>3.0.CO;2-# doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1565(199603)7:2<69::AID-PCA290>3.0.CO;2-#
- ↑ Arora R. Isolation and characterization of 1,3-dicapryloyl-2-linoleoylglycerol: a novel triglyceride from berries of Hippophae rhamnoides // Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin — Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, 2005. — Vol. 53, Iss. 8. — P. 1021–1024. — ISSN 0009-2363; 1347-5223 — doi:10.1248/CPB.53.1021
- ↑ Kallio H., Yang B. Effects of different origins and harvesting time on vitamin C, tocopherols, and tocotrienols in sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides) berries // J. Agric. Food Chem. — USA: ACS, 2002. — Vol. 50, Iss. 21. — P. 6136–6142. — ISSN 0021-8561; 1520-5118 — doi:10.1021/JF020421V
- ↑ а б Chen I. Chemical and cytotoxic constituents from Peperomia sui // Phytochemistry — Elsevier BV, 2003. — Vol. 63, Iss. 5. — P. 603–608. — 6 p. — ISSN 0031-9422; 1873-3700 — doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00183-3
- ↑ а б в г Boyes S., Strübi P., Marsh H. Sugar and Organic Acid Analysis of Actinidia arguta and Rootstock–Scion Combinations of Actinidia arguta // Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. — Elsevier BV, 2002. — Vol. 30, Iss. 4. — P. 390–397. — ISSN 0023-6438; 1096-1127 — doi:10.1006/FSTL.1996.0201
- ↑ а б в г д е Vinci G., Botrè F., Mele G. et al. Ascorbic acid in exotic fruits: a liquid chromatographic investigation // Food Chem. — Elsevier BV, 2002. — Vol. 53, Iss. 2. — P. 211–214. — ISSN 0308-8146; 1873-7072 — doi:10.1016/0308-8146(95)90791-5
- ↑ а б D. Guo, Xue W. J., Zou G. A. et al. Chemical Composition of Alhagi sparsifolia Flowers // Chemistry of Natural Compounds — Springer Science+Business Media, 2016. — Vol. 52, Iss. 6. — P. 1095–1097. — ISSN 0009-3130; 1573-8388 — doi:10.1007/S10600-016-1871-5
- ↑ а б в г д е ё ж з і к л м н о п р с т у ф х Batanouny K. H. Adaptation of Desert Plants — 2013. — С. 39–44. — doi:10.1007/978-3-662-04480-3_6
- ↑ M.L.C.M.M. Alarcão-E-Silva, A.E.B. Leitão, H.G. Azinheira et al. The Arbutus Berry: Studies on its Color and Chemical Characteristics at Two Mature Stages // J. Food Comp. Anal. — Elsevier BV, 2001. — Vol. 14, Iss. 1. — P. 27–35. — ISSN 0889-1575; 1096-0481 — doi:10.1006/JFCA.2000.0962
- ↑ а б в г д Barale R. Vegetables inhibit, in vivo, the mutagenicity of nitrite combined with nitrosable compounds // Mutation Research — Elsevier BV, 1983. — Vol. 120, Iss. 2-3. — P. 145–150. — ISSN 1383-5718; 0027-5107 — doi:10.1016/0165-7992(83)90156-2
- ↑ а б WU Y., PERRY A. K., KLEIN B. P. VITAMIN C AND ?-CAROTENE IN FRESH AND FROZEN GREEN BEANS AND BROCCOLI IN A SIMULATED SYSTEM // J. Food Qual. — Wiley-Blackwell, Hindawi Publishing Corporation, 2007. — Vol. 15, Iss. 2. — P. 87–96. — ISSN 0146-9428; 1745-4557 — doi:10.1111/J.1745-4557.1992.TB00977.X
- ↑ а б Fishman G. M., Bandyukova V. A. Chemical composition of the leaves of Camellia sasanqua // Chemistry of Natural Compounds — Springer Science+Business Media, 2004. — Vol. 27, Iss. 3. — P. 371–371. — ISSN 0009-3130; 1573-8388 — doi:10.1007/BF00630333
- ↑ а б в Cherng J., Shih M. Preventing dyslipidemia by Chlorella pyrenoidosa in rats and hamsters after chronic high fat diet treatment // Life Sci. — Elsevier BV, 2005. — Vol. 76, Iss. 26. — P. 3001–3013. — ISSN 0024-3205; 1879-0631 — doi:10.1016/J.LFS.2004.10.055
- ↑ а б в г д е ё VITAMIN CONTENT OF DRIED FRUITS // Science / H. Thorp — Northern America: AAAS, 1929. — Vol. 70, Iss. 1803. — P. x. — ISSN 0036-8075; 1095-9203 — doi:10.1126/SCIENCE.70.1803.0X-S
- ↑ M.S. AL-SAIKHAN, L.R. HOWARD, J.C. MILLER Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolics in Different Genotypes of Potato (Solanum tuberosum, L.) // Journal of Food Science — Institute of Food Technologists, 2006. — Vol. 60, Iss. 2. — P. 341–343. — ISSN 0022-1147; 1750-3841 — doi:10.1111/J.1365-2621.1995.TB05668.X
- ↑ Yen G. C., Hsieh C. L. Reactive oxygen species scavenging activity of Du-zhong (Eucommia ulmoides oliv.) and its active compounds // J. Agric. Food Chem. — USA: ACS, 2000. — Vol. 48, Iss. 8. — P. 3431–3436. — ISSN 0021-8561; 1520-5118 — doi:10.1021/JF000150T
- ↑ Jr R. F. A neglected Mayan galactagogue - ixbut (Euphorbia lancifolia). // J. Ethnopharmacol. — Elsevier BV, 1982. — Vol. 5, Iss. 1. — P. 91–112. — ISSN 0378-8741; 1872-7573 — doi:10.1016/0378-8741(82)90024-1
- ↑ Rosengarten F. A Neglected Mayan Galactagogue. Ixbut (Euphorbia lancifolia) // Botanical Museum Leaflets — Cambridge, Mass: 2021. — Vol. 26, Iss. 9--10. — P. 277–309. — ISSN 0006-8098 — doi:10.5962/P.295216
- ↑ Ascorbic acid deficiency — 2011. — doi:10.1007/SPRINGERREFERENCE_37610
- ↑ Rapid method for determining ascorbic acid concentration // Jour. of the Franklin Inst. — Elsevier BV, 2003. — Vol. 231, Iss. 3. — P. 287. — ISSN 0016-0032; 1879-2693 — doi:10.1016/S0016-0032(41)90055-8
- ↑ а б в Vendramini A. L., Trugo L. C. Chemical composition of acerola fruit (Malpighia punicifolia L.) at three stages of maturity // Food Chem. — Elsevier BV, 2000. — Vol. 71, Iss. 2. — P. 195–198. — ISSN 0308-8146; 1873-7072 — doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00152-7
- ↑ Lalaguna F. Purification of fresh cassava root polyphenols by solid-phase extraction with Amberlite XAD-8 resin // J. Chromatogr. A — Elsevier BV, 2002. — Vol. 657, Iss. 2. — P. 445–449. — ISSN 1873-3778; 0021-9673 — doi:10.1016/0021-9673(93)80301-N
- ↑ Yen G. C., Duh P. D., Hung Y. L. Contributions of major components to the antimutagenic effect of Hsian-tsao (Mesona procumbens Hemsl.). // J. Agric. Food Chem. — USA: ACS, 2001. — Vol. 49, Iss. 10. — P. 5000–5004. — ISSN 0021-8561; 1520-5118 — doi:10.1021/JF0103929
- ↑ Prasad T. K., Dave Y. S., Mehta P. M. Ontogeny and histochemistry of axillary bud inMurraya koenigii L. spreng // Biologia Plantarum: journal for experimental botany — Springer Science+Business Media, Institute of Experimental Botany of the Czech Academy of Sciences, 2008. — Vol. 23, Iss. 2. — P. 91–97. — ISSN 0006-3134; 1573-8264 — doi:10.1007/BF02878410
- ↑ Dugo G. Chemical characterization and biological effects of Sicilian Opuntia ficus indica (L.) mill. Fruit juice: antioxidant and antiulcerogenic activity // J. Agric. Food Chem. — USA: ACS, 2003. — Vol. 51, Iss. 17. — P. 4903–4908. — ISSN 0021-8561; 1520-5118 — doi:10.1021/JF030123D
- ↑ R. Yasmin, Naru A. M. Biochemical analysis of Papaver somniferum (opium poppy), Biochemical analysis of Papaver soniferum (opium poppy) // Biochem. Soc. Trans. — Portland Press, 1991. — Vol. 19, Iss. 4. — P. 436S. — ISSN 0300-5127; 1470-8752 — doi:10.1042/BST019436S
- ↑ Johannes P.F.G. Helsper, Loewus F. A. Studies on l-ascorbic acid biosynthesis and metabolism in Parthenocissus quinquefolia L. (vitaceae) // Plant Science — Elsevier BV, 2003. — Vol. 40, Iss. 2. — P. 105–109. — ISSN 0168-9452; 1873-2259 — doi:10.1016/0168-9452(85)90049-4
- ↑ Roy A. K., Dhir H., Sharma A. et al. Phyllanthus emblica Fruit Extract and Ascorbic Acid modify Hepatotoxic and Renotoxic Effects of Metals in Mice // International journal of pharmacognosy — 2007. — Vol. 29, Iss. 2. — P. 117–126. — ISSN 0925-1618 — doi:10.3109/13880209109082862
- ↑ Kostman T. A., Tarlyn N. M., Loewus F. A. et al. Biosynthesis of L-ascorbic acid and conversion of carbons 1 and 2 of L-ascorbic acid to oxalic acid occurs within individual calcium oxalate crystal idioblasts // Plant Physiol. — American Society of Plant Biologists, 2001. — Vol. 125, Iss. 2. — P. 634–40. — ISSN 0032-0889; 1532-2548 — doi:10.1104/PP.125.2.634
- ↑ Simopoulos A. P., Norman H. A., Gillaspy J. E. et al. Common purslane: a source of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants // Journal of the American College of Nutrition — Taylor & Francis, 1992. — Vol. 11, Iss. 4. — P. 374–382. — ISSN 0731-5724; 1541-1087 — doi:10.1080/07315724.1992.10718240
- ↑ Nergiz C., Yıldız H. Research on Chemical Composition of Some Varieties of European Plums (Prunus domestica) Adapted to the Aegean District of Turkey // J. Agric. Food Chem. — USA: ACS, 2002. — Vol. 45, Iss. 8. — P. 2820–2823. — ISSN 0021-8561; 1520-5118 — doi:10.1021/JF970032E
- ↑ Bulk R. E. E., El Fadil E. Babiker, Tinay A. H. E. Changes in chemical composition of guava fruits during development and ripening // Food Chem. — Elsevier BV, 2002. — Vol. 59, Iss. 3. — P. 395–399. — ISSN 0308-8146; 1873-7072 — doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(96)00271-3
- ↑ Liso R., Calabrese G. Research on ascorbic acid physiology in red algae. 2. Dehydroascorbic acid compartmentation in the cell // Phycologia — Allen Press, Taylor & Francis, 2010. — Vol. 13, Iss. 3. — P. 205–208. — ISSN 0031-8884; 2330-2968 — doi:10.2216/I0031-8884-13-3-205.1
- ↑ B. Bozan, Sagdullaev B. T., M. Kozar et al. Comparison of ascorbic and citric acid contents inRosa canina L. fruit growing in the Central Asian region // Chemistry of Natural Compounds — Springer Science+Business Media, 2006. — Vol. 34, Iss. 6. — P. 687–689. — ISSN 0009-3130; 1573-8388 — doi:10.1007/BF02336094
- ↑ а б в г S. Kurucu, M. Coşskun, M. Kartal High Pressure Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Ascorbic Acid in the Fruits of SomeRosaSpecies Growing in Turkey // Planta Med. — Thieme Medical Publishers (Germany), 2008. — Vol. 58, Iss. S 1. — P. 675–676. — ISSN 0032-0943; 1439-0221 — doi:10.1055/S-2006-961691
- ↑ Bikbulatova T. N., Beisekova K. D. Chemical composition of the fruit ofRosa platyacantha // Chemistry of Natural Compounds — Springer Science+Business Media, 2004. — Vol. 15, Iss. 3. — P. 372–372. — ISSN 0009-3130; 1573-8388 — doi:10.1007/BF00566112
- ↑ а б Kuliev V. B., Gusarova N. V. Components of the fruit ofRosa nisami // Chemistry of Natural Compounds — Springer Science+Business Media, 1984. — Vol. 20, Iss. 4. — P. 513–514. — ISSN 0009-3130; 1573-8388 — doi:10.1007/BF00574362
- ↑ Plekhanova T. I., Bandyukova V. A., F. Kh. Bairamkulova Chemical components of the fruit ofRosa spinosissima // Chemistry of Natural Compounds — Springer Science+Business Media, 2004. — Vol. 14, Iss. 3. — P. 334–334. — ISSN 0009-3130; 1573-8388 — doi:10.1007/BF00713334
- ↑ Omarova M. A., Artamonova N. A., Chasovitina G. M. Chemical composition of the hybrid Rumex K-1 // Chemistry of Natural Compounds — Springer Science+Business Media, 2006. — Vol. 34, Iss. 4. — P. 426–428. — ISSN 0009-3130; 1573-8388 — doi:10.1007/BF02329587
- ↑ а б J. Karovičová, J. Polonský, A. Príbela Composition of organic acids of Sambucus nigra and Sambucus ebulus // Mol. Nutr. Food Res. — Wiley-Blackwell, 2006. — Vol. 34, Iss. 7. — P. 665–667. — ISSN 1613-4125; 1613-4133 — doi:10.1002/FOOD.19900340716
- ↑ BUSHWAY R. J., BUREAU J. L., MCGANN D. F. Determinations of Organic Acids in Potatoes by High Performance Liquid Chromatography // Journal of Food Science — Institute of Food Technologists, 2006. — Vol. 49, Iss. 1. — P. 76–77. — ISSN 0022-1147; 1750-3841 — doi:10.1111/J.1365-2621.1984.TB13673.X
- ↑ Min K., Chen K., Arora R. A metabolomics study of ascorbic acid-induced in situ freezing tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). // Plant direct — Wiley, 2020. — Vol. 4, Iss. 2. — P. e00202. — ISSN 2475-4455 — doi:10.1002/PLD3.202
- ↑ а б SAWAYA W. N., A. AL-SHALHAT, A AL-SOGAIR et al. Chemical Composition and Nutritive Value of Truffles of Saudi Arabia // Journal of Food Science — Institute of Food Technologists, 2010. — Vol. 50, Iss. 2. — P. 450–453. — ISSN 0022-1147; 1750-3841 — doi:10.1111/J.1365-2621.1985.TB13425.X
- ↑ Z. El-Hawary, El-Shobaki F. A. Vitamins content of fruits and vegetables in common use in Egypt // European Journal of Nutrition — Springer Science+Business Media, 1977. — Vol. 16, Iss. 3. — P. 158–162. — 5 p. — ISSN 1436-6207; 1436-6215; 0044-264X; 1435-1293 — doi:10.1007/BF02024787
- ↑ Seeram N. P. Total cranberry extract versus its phytochemical constituents: antiproliferative and synergistic effects against human tumor cell lines // J. Agric. Food Chem. — USA: ACS, 2004. — Vol. 52, Iss. 9. — P. 2512–2517. — ISSN 0021-8561; 1520-5118 — doi:10.1021/JF0352778
- ↑ Abu J. D. DEVELOPMENT OF A SWEETENER FROM BLACK PLUM (VITEX DONIANA) FRUIT // International Journal of Food Properties — Marcel Dekker, Taylor & Francis, 2002. — Vol. 5, Iss. 1. — P. 153–159. — ISSN 1094-2912; 1532-2386 — doi:10.1081/JFP-120015598
- ↑ Conklin P. L. Recent advances in the role and biosynthesis of ascorbic acid in plants // Plant, Cell and Environment / A. Amtmann — Wiley-Blackwell, 2001. — Vol. 24, Iss. 4. — P. 383–394. — ISSN 0140-7791; 1365-3040 — doi:10.1046/J.1365-3040.2001.00686.X
- ↑ Jones O. Mixtures of similarly acting compounds in Daphnia magna: from gene to metabolite and beyond // Environ. Int. — Elsevier BV, 2010. — Vol. 36, Iss. 3. — P. 254–268. — ISSN 0160-4120; 1873-6750 — doi:10.1016/J.ENVINT.2009.12.006
- ↑ Nielsen J. B., Westerhoff H., Kell D. et al. A community-driven global reconstruction of human metabolism // Nature Biotechnology — NPG, 2013. — Vol. 31, Iss. 5. — P. 419–425. — ISSN 1087-0156; 1546-1696 — doi:10.1038/NBT.2488
- ↑ Gardiner N. J., Lakshmanan M., Martínez V. S. et al. Recon 2.2: from reconstruction to model of human metabolism // Metabolomics — Springer Science+Business Media, 2016. — Vol. 12, Iss. 7. — P. 109. — ISSN 1573-3882; 1573-3890 — doi:10.1007/S11306-016-1051-4
- ↑ Naik G. H., Priyadarsini K. I., Naik D. B. et al. Studies on the aqueous extract of Terminalia chebula as a potent antioxidant and a probable radioprotector // Phytomedicine — Elsevier BV, 2004. — Vol. 11, Iss. 6. — P. 530–538. — ISSN 0944-7113; 1618-095X — doi:10.1016/J.PHYMED.2003.08.001
- ↑ Doka I. G., Tigani S. E., Yagi S. Nutritional Profile and Radical Scavenging Capacity of Tubers of Two Dioscorea Species // Advance journal of food science and technology : AJFST — 2016. — Vol. 11, Iss. 3. — P. 262–268. — ISSN 2042-4868; 2042-4876 — doi:10.19026/AJFST.11.2408
- ↑ P.S. Krishnamurty Niesanfälle - Stachys betonica // Zeitschrift für klassische Homöopathie — 2017. — Т. 33, вып. 05. — S. 200–201. — ISSN 0935-0853; 1439-4308 — doi:10.1055/S-2006-938336
- ↑ Perino J. V. Osage orange (Maclura pomifera): History and economic uses // Econ. Bot. — Springer Science+Business Media, 1981. — Vol. 35, Iss. 1. — P. 24–41. — ISSN 0013-0001; 1874-9364 — doi:10.1007/BF02859211
- ↑ Novère N. L., Witting M., Hastings J. et al. Modeling Meets Metabolomics-The WormJam Consensus Model as Basis for Metabolic Studies in the Model Organism // Frontiers in molecular biosciences — Frontiers Media, 2018. — Vol. 5. — P. 96. — ISSN 2296-889X — doi:10.3389/FMOLB.2018.00096
- ↑ Eloisa Helena A. Andrade, Maria das Graças B. Zoghbi, José Guilherme S. Maia et al. Chemical Characterization of the Fruit of Annona squamosa L. Occurring in the Amazon // J. Food Comp. Anal. — Elsevier BV, 2002. — Vol. 14, Iss. 2. — P. 227–232. — ISSN 0889-1575; 1096-0481 — doi:10.1006/JFCA.2000.0968
- ↑ Tomás-Barberán F. A. Effect of Modified Atmosphere Packaging on the Flavonoids and Vitamin C Content of Minimally Processed Swiss Chard (Beta vulgarisSubspeciescycla) // J. Agric. Food Chem. — USA: ACS, 1998. — Vol. 46, Iss. 5. — P. 2007–2012. — ISSN 0021-8561; 1520-5118 — doi:10.1021/JF970924E
- ↑ Pietrzkowski Z., Spórna A., Michałowski T. et al. Betalainic and nutritional profiles of pigment-enriched red beet root (Beta vulgaris L.) dried extracts // Food Chem. — Elsevier BV, 2010. — Vol. 127, Iss. 1. — P. 42–53. — ISSN 0308-8146; 1873-7072 — doi:10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2010.12.081
- ↑ Sgherri C., Navari-Izzo F. Phenols and antioxidative status of Raphanus sativus grown in copper excess // Physiol. Plant. — Wiley-Blackwell, 2003. — Vol. 118, Iss. 1. — P. 21–28. — ISSN 0031-9317; 1399-3054 — doi:10.1034/J.1399-3054.2003.00068.X
- ↑ Goyeneche R., Roura S., Ponce A. et al. Chemical characterization and antioxidant capacity of red radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and roots // Journal of Functional Foods — Elsevier BV, 2015. — Vol. 16. — P. 256–264. — ISSN 1756-4646; 2214-9414 — doi:10.1016/J.JFF.2015.04.049
- ↑ Kim Y., Joo S. C., Shi J. et al. Metabolic dynamics and physiological adaptation of Panax ginseng during development // Plant Cell Rep. — Springer Science+Business Media, 2017. — Vol. 37, Iss. 3. — P. 393–410. — ISSN 1432-203X; 0721-7714 — doi:10.1007/S00299-017-2236-7
- ↑ Chitrakar B., Zhang M., Adhikari B. Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis): Processing effect on nutritional and phytochemical composition of spear and hard-stem byproducts // Trends in Food Science and Technology — Elsevier BV, 2019. — Vol. 93. — P. 1–11. — ISSN 0924-2244; 1879-3053 — doi:10.1016/J.TIFS.2019.08.020
- ↑ Hashimoto M., Matsuzaki K., Katakura M. Intake of Alpha-Linolenic Acid-Rich Perilla frutescens Leaf Powder Decreases Home Blood Pressure and Serum Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Japanese Adults // Molecules — MDPI, 2020. — Vol. 25, Iss. 9. — ISSN 1420-3049; 1431-5157 — doi:10.3390/MOLECULES25092099
- ↑ Hamrouni-Sellami I., Rahali F. Z., Rebey I. B. et al. Total Phenolics, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Activity of Sage (Salvia officinalis L.) Plants as Affected by Different Drying Methods // Food and Bioprocess Technology — Springer Science+Business Media, 2012. — Vol. 6, Iss. 3. — P. 806–817. — ISSN 1935-5130; 1935-5149 — doi:10.1007/S11947-012-0877-7
- ↑ Sanni O., Koorbanally N. A., Erukainure O. L. Azadirachta indica inhibits key enzyme linked to type 2 diabetes in vitro, abates oxidative hepatic injury and enhances muscle glucose uptake ex vivo // Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy — Elsevier BV, 2018. — Vol. 109. — P. 734–743. — ISSN 0753-3322; 1950-6007 — doi:10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2018.10.171
- ↑ Liu R. H. Phytochemical profiles and antioxidant activity of wheat varieties // J. Agric. Food Chem. — USA: ACS, 2003. — Vol. 51, Iss. 26. — P. 7825–7834. — ISSN 0021-8561; 1520-5118 — doi:10.1021/JF030404L
- ↑ Calhelha R. C., Santos-Buelga C., Barros L. et al. Chemical characterisation and bioactive properties of Prunus avium L.: The widely studied fruits and the unexplored stems // Food Chem. — Elsevier BV, 2015. — Vol. 173. — P. 1045–1053. — ISSN 0308-8146; 1873-7072 — doi:10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2014.10.145
- ↑ (not translated to mul), (not translated to mul) Postharvest responses of sweet cherry fruit and stem tissues revealed by metabolomic profiling // Plant Physiology and Biochemistry — (untranslated), 2018. — Т. 127. — С. 478–484. — 7 с. — ISSN 0981-9428; 1873-2690 — doi:10.1016/J.PLAPHY.2018.04.029
- ↑ а б в г López-Palestina C. U. Nutritional Composition, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Wild Edible Flowers Consumed in Semiarid Regions of Mexico // Plant Foods for Human Nutrition — Springer Science+Business Media, 2020. — ISSN 0921-9668; 1573-9104 — doi:10.1007/S11130-020-00822-2
- ↑ Skrede G., Martinsen B. K., Wold A. et al. Variation in quality parameters between and within 14 Nordic tree fruit and berry species // Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B: Soil & Plant Science — Stockholm: Taylor & Francis, 2011. — Vol. 62, Iss. 3. — P. 193–208. — ISSN 0906-4710; 1651-1913 — doi:10.1080/09064710.2011.598543
- ↑ K. SKUPIEN, J. OSZMIANSKI The effect of mineral fertilization on nutritive value and biological activity of chokeberry fruit // Agricultural and Food Science — Scientific Agricultural Society of Finland, Agricultural Research Centre, Agrifood Research Finland, 2008. — Т. 16, вып. 1. — С. 46. — ISSN 1459-6067; 1239-0992; 1795-1895 — doi:10.2137/145960607781635822
- ↑ Wang B., Li X. Antioxidant Hydroanthraquinones from the Marine Algal-Derived Endophytic Fungus Talaromyces islandicus EN-501 // J. Nat. Prod. — ACS, 2016. — Vol. 80, Iss. 1. — P. 162–168. — ISSN 0163-3864; 1520-6025 — doi:10.1021/ACS.JNATPROD.6B00797
- ↑ Chen C., Shaw C., Chen C. et al. 2,3,4-Trimethyl-5,7-dihydroxy-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran, a novel antioxidant, from Penicillium citrinum F5. // J. Nat. Prod. — ACS, 2002. — Vol. 65, Iss. 5. — P. 740–741. — ISSN 0163-3864; 1520-6025 — doi:10.1021/NP010605O
- ↑ Takamatsu S., Ferreira D., Khan I. A. Schisandrene, a dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan from Schisandra chinensis: structure-antioxidant activity relationships of dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans // J. Nat. Prod. — ACS, 2006. — Vol. 69, Iss. 3. — P. 356–359. — ISSN 0163-3864; 1520-6025 — doi:10.1021/NP0503707
- ↑ Jacquemin D., Ferron S., Pogam P. L. et al. Minor Pyranonaphthoquinones from the Apothecia of the Lichen Ophioparma ventosa // J. Nat. Prod. — ACS, 2016. — Vol. 79, Iss. 4. — P. 1005–1011. — ISSN 0163-3864; 1520-6025 — doi:10.1021/ACS.JNATPROD.5B01073
- ↑ BUSHWAY A. A., SERREZE D. V., McGANN D. F. et al. Effect of Processing Method and Storage Time on the Nutrient Composition of Fiddlehead Greens // Journal of Food Science — Institute of Food Technologists, 2006. — Vol. 50, Iss. 5. — P. 1491–1492. — ISSN 0022-1147; 1750-3841 — doi:10.1111/J.1365-2621.1985.TB10508.X
- ↑ Zhou X., Wang J., Liu Y. Spiro-Phthalides and Isocoumarins Isolated from the Marine-Sponge-Derived Fungus Setosphaeria sp. SCSIO41009 // J. Nat. Prod. — ACS, 2018. — Vol. 81, Iss. 8. — P. 1860–1868. — ISSN 0163-3864; 1520-6025 — doi:10.1021/ACS.JNATPROD.8B00345
- ↑ Cichewicz R. H. Chlorinated polyketide obtained from a Daldinia sp. treated with the epigenetic modifier suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid // J. Nat. Prod. — ACS, 2014. — Vol. 77, Iss. 11. — P. 2454–2458. — ISSN 0163-3864; 1520-6025 — doi:10.1021/NP500522Z
- ↑ LiverTox Праверана 8 красавіка 2021.
Літаратура
[правіць | правіць зыходнік]- Хімічны слоўнік навучэнца: дапаможнік для вучняў / Б. М. Качаргін, В. М. Макарэўскі, Л. Я. Гарнастаева, В. С. Аранская. — Мінск: Народная асвета, 2003. — С. 40—41. — 287 с. — 1 000 экз. — ISBN 985-12-0631-8.
Спасылкі
[правіць | правіць зыходнік]- Аскорбиновая кислота* (Ascorbic acid*)(недаступная спасылка) // Регистр лекарственных средств России (руск.)
- Аскорбиновая кислота* // Реестр лекарственных средств (руск.)
 На Вікісховішчы ёсць медыяфайлы па тэме Аскарбінавая кіслата
На Вікісховішчы ёсць медыяфайлы па тэме Аскарбінавая кіслата